休斯顿中城公园
美国 / Design Workshop, Inc.
“在表演凉亭、小径、集市、餐厅、艺术花园、遛狗公园和社交游戏场地的作用下,曾经缺乏活跃度的草坪如今重新变得生机勃勃。以河弯为灵感的水景将大自然带入城市,为人们提供了休憩空间和可持续的水资源管理——所有的一切都建造在地下公共停车场的屋顶之上。雨水被收集并储存在一个容量为7万加仑的地下蓄水池中。中城公园是一个初期的示范性项目,将使休斯顿成为一个更加环保和步行友好的城市。”
– 2022年评审委员会
“The once underused lawn is now activated with a performance pavilion, trails, marketplace, two restaurants, an arts garden, dog park, and social game courts. Bayou-inspired water features bring nature to the city to provide respite and sustainable water management – all built on top of a public underground parking garage. Rainwater is collected and stored within a 70,000-gallon subsurface cistern. Midtown Park serves as an early demonstration project for the ongoing development of a greener, more walkable Houston.”
– 2022 Awards Jury
来自 ASLA 对gooood的分享。
2022 ASLA URBAN DESIGN AWARD OF HONOR: Midtown Park | Design Workshop, Inc.
项目陈述
Project Statement
中城公园的开放标志着休斯顿中城区十年来的复兴梦想终于成为现实。2010年,中城重建局(MRA)与设计团队共同为这一曾经在历史上陷入困境的社区制定了发展战略。计划提出通过具有催化性的项目来帮助克服该社区所面临的社会、环境和经济差距问题。由于休斯顿缺乏分区规划且基础设施日渐老化,该地区亟需重建凝聚力、增加理想的经济适用房、提高连通性并创造开放的绿色空间。作为计划中的压轴项目,中城公园将以上所有因素整合在一起,如今已成为休斯顿“最适合步行的社区”中的首选目的地。
中城公园超级街区提供了亟需的住房、商业空间和(地下)路外停车位,并配套以自然区域、艺术区、雨水节流区和社区集会空间,这座充满活力的城市公园改善了游客对绿地和各类设施的使用体验,同时在公园具有标志性的空间内实现了主动与被动休闲机会的平衡。中城公园是休斯顿的第一个SITES项目,它代表了美国最大、最多元化的城市之一所具备的可持续性与恢复力。
The opening of Midtown Park fulfills a decade long dream to rejuvenate Midtown Houston. In 2010, the Midtown Redevelopment Authority (MRA) and design team strategized revitalizing this neighborhood, which historically struggled. A vision plan was adopted that identified catalyst projects to help overcome the social, environmental, and economic disparities plaguing the community. Facilitated by Houston’s absence of zoning and aging infrastructure, the district lacked cohesiveness, desirable and affordable housing, connectivity, and green open spaces. The capstone project, Midtown Park, brings these elements together as the premier destination for the (now) “most walkable neighborhood” in Houston.
The Midtown Park superblock provides much-needed housing, commercial space, and (subsurface) off-street parking as well as nature, art, stormwater detention, and community gathering areas. This vibrant, urban park improves access to green space and amenities for visitors while creating a balance of active and passive recreational opportunities within the park’s signature spaces. Slated to be the first SITES project in Houston, Midtown Park represents sustainability and resilience in one of the nation’s largest and most diverse cities.

▲中城公园:在过去的50年间,中城的复兴计划曾被多次提出。设计团队通过场所营造确立了社区特色,解决了基础设施老化的问题,为所有家庭与企业创造了一个公平的、国际化的新社区。Midtown Park. Many attempts were made to revitalize Midtown Houston over the past five-decades. Through placemaking the design team established community character and addressed aging infrastructure to create a new equitable, cosmopolitan community for all families and businesses.
项目说明
Project Narrative
许多人都对休斯顿缺乏分区、洪水多发的状况有所耳闻,但很少有人知道休斯顿是美国最多元化的城市。设计团队受中城重建局(MRA)的委托对中城区进行重新规划,旨在将其打造为一个充满活力、以行人为导向的多功能中心。通过战略规划和一系列催化项目的投资,如今的中城已经成为休斯顿最适合步行的区域。中城公园作为本次规划的最终成果,为居民与游客提供了一个真正意义上的城市公园。
在过去的50年,中城的复兴计划被多次提出,但由于缺乏鲜明的社区特色和特征,加上基础设施的老化,导致新的商业不断迁往成本效益更高的郊区。1990年代,中城重建局(MRA)在基层民众的努力下得以成立,这是一个致力于地区发展与繁荣的组织。成立之后,MRA立即向市政府提出申请,要求将中城建设为以艺术和娱乐为特色的城区,并由税收增量再投资区(TIRZ)提供支持。这项倡议为中城的发展奠定了基础。凭借着优越的地理位置、TIRZ的资助以及新的规划策略,中城区已经做好了充分发挥其潜力的准备。
全面的复兴工作开始于2010年的宜居市中心研究(Livable Center Study),该研究旨在提出能够为中城区注入全新活力的战略建议。设计团队创建了一份愿景计划,将重点放在城市设计机制和试点项目的确定,帮助社区解决社会、环境和经济问题并展示艺术作品。该计划还针对休斯顿缺乏分区和基础设施老化的问题提出了解决建议。设计团队将场所的营造与复原力作为成功落实项目的关键因素。作为这些项目的最终成果,中城公园如今已成为休斯顿“最适合步行的社区”中的首选目的地。
愿景
中城区“中央公园”的概念是在MRA成立时提出的。作为休斯顿的改革机构,MRA的工作包括收购未被充分利用的地产以抓住发展机遇。在完成收购之后,MRA、开发商与设计团队经过了为期数年的合作,将这处地产开发为城市区域内的活动和集会中心。
环境
中城公园地处休斯顿中城区的中心地带,是一个不断成长的街区,凭借着公共领域的再开发而被赋予了崭新的面貌。该项目占地6英亩,被称为“超级街区”,这里主要分布着交通不便且缺乏维护的私有空地,狭窄的人行道和几棵被保留下来的高大橡树定义出场地的边界。中城公园是该场地与更大范围的公园系统的核心,它占地3英亩,设有表演亭、小径、集市、游乐场、互动喷泉、艺术花园、遛狗公园和社交游戏场地。以河湾为灵感的水景为城市带来了大自然的气息,同时也提供了可持续的水资源管理——所有的一切都建造在地下公共停车场的屋顶之上。中城公园是休斯顿向“更环保、更适合步行的城市”发展进程中的示范性项目,它证明了高质量的公共空间是成功打造宜居城市的关键要素。
面对打造“中城区首选城市公园”的挑战,设计团队认识到公园需要与其所在的地区无缝地融合在一起。他们充分利用场地的地理位置、交通便利、周边的开发项目以及在地下设置停车场的需求,并成功与当地组织进行合作,完成了公园的设计和建造。落成后的公园不仅满足了附近居民与更大范围的社区的需求,还通过规划和创新设计提升了该地区品牌形象的完整性。
中城区位于市中心与医疗中心这两大就业中心之间。休斯顿是全美国公园数量最少的城市之一。为了促进区域发展,中城区政府进行了公共街景投资,这也让中城公园成为了休斯顿城市结构中的重要目的地。
特征
公园紧邻休斯顿以公共交通为导向的主街,战略性的位置确保了其始终能够作为一个公平的资源。中城公园紧邻公交、轻轨和自行车共享系统,已经迅速成为该地区最受欢迎和游览频率最高的开放空间之一,公园的游客也充分彰显了休斯顿作为美国文化最多元城市的称号。
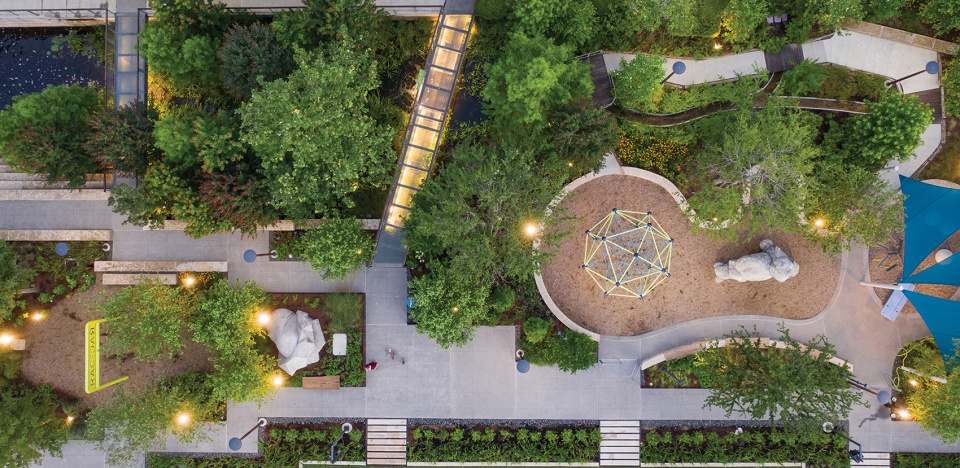
中城公园由各种灵活的多功能空间构成,可以容纳丰富的活动和计划,如集市和节庆活动等,它们为周边社区创造了经济增长,并树立了社区意识。为了支持中城战略规划和中城开放空间规划,公园的设计旨在让所有年龄段的人都能参与其中。为了使公园得到持续的改进,设计和布局侧重于灵活性的使用,特别是位于中央的大型多功能草坪,它坡度平缓,面对着舞台旁边的“雨水喷泉”(通过“雨滴”和“闪电”的场景编排来模拟休斯顿的暴风雨)。在不运作时,喷泉可以变成额外的广场空间,并在活动期间提供灵活的座位。
公共艺术是公园设计中的一个重要组成部分,并渗透到了园内的每个角落。中城公园保护协会投入巨资,邀请来自当地且在国际上知名的艺术家设计了4件永久艺术作品,使公园成为该地区标志性的存在。
位于活动草坪后方的护堤为地势平坦的区域提供了地形上的缓冲,使人们可以欣赏市中心天际线的景色。护堤的存在并未影响公园的通达感,在极佳的照明条件下,公园的各个角落和主要人行道的边缘(如主街)始终保持透明,从而能够超越边界,融入多样化的社区。
事实证明,创造一个能让树木和花园茁壮生长的环境,同时在地下停车场的顶部维持一个具有生命力的、可持续的公园,是一项可以克服的挑战。公园的停车场具有复杂的排水系统、坚固的防水层、水泵和雨水蓄水池。地下停车场的设计既是机遇也是挑战,因为在一个开发压力极大、几乎不能设置地上车位的区域,整合亟需的停车场有助于提升该项目的可行性。
恢复力
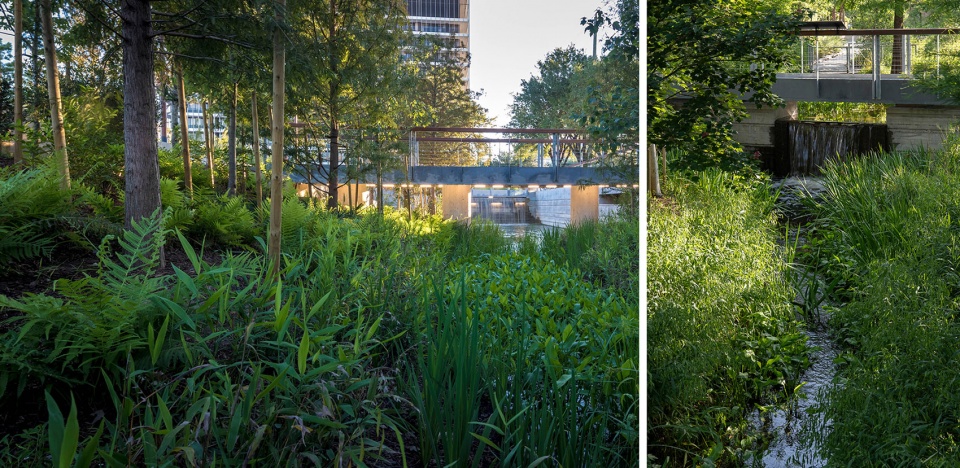
场地的主线和设计的关键特征在于对“河湾”的整合。这是一个人造的水道和滞留系统,模仿了休斯顿的天然河口、沼泽、低地硬木森林和湿地,它们均是当地水文不可或缺的组成部分。公园的教育功能与生态湿地和雨水花园相结合,在设计时使用了容易在环境中找到的各种本地材料,证明了其在改善水质和野生动物栖息地的同时,还能够防止洪水泛滥,从而增强经济与生态复原力。在哈维飓风等极端降雨事件发生期间,河湾可以吸收并滞留雨水,从而防止当地洪泛和财产损失。
雨水被收集并储存在一个容量为7万加仑的地下蓄水池中。雨水可在现场重复使用,例如灌溉植物材料,或作为中城河湾循环的“补给”水。当存在多余的水时,例如在大雨期间,一个溢流结构会将水直接输送到人工建造的河湾,使水在经过植物和土壤的维持和处理后排入城市的雨水沟渠系统。这种分层式的、综合的雨水管理方法减轻了基础设施系统的压力,有助于通过自然渗透净化水质。作为中城区最重要的公园景点,成功整合高度复杂的雨水管理系统,并承诺以负责任的方式使用资源,对于该项目有着至关重要的意义。公园的可持续发展措施为休斯顿市民提供了一种全新模式——同时它也获得了SITES的银级认证。

▲规划图:战略性的规划和催化项目的开发使中城区成为了休斯顿最适宜步行的居住地。中城公园实现了20年前制定的愿景,为社区提供了一个集娱乐、艺术、自然和聚会为一体的中央城市公园。Planning. Strategic planning and catalyst developments has made Midtown District the most walkable place to live in Houston. Fulfilling a vision established 20 years ago, Midtown Park provides its community a central urban park defined, by recreation, art, nature, and gathering.
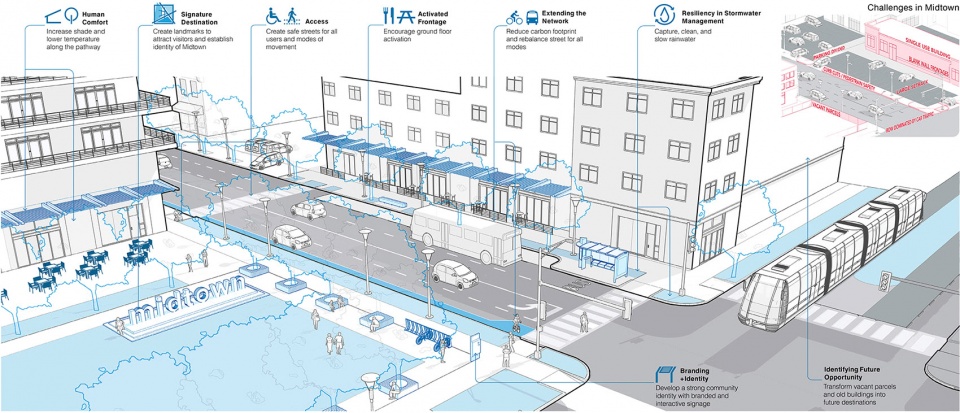
▲经济可行性:被采用的愿景规划为克服休斯顿缺乏分区以及社会、经济和环境方面的问题提供了城市设计建议,这对该地区有着至关重要的意义。成倍增长的再投资为中城公园的开发奠定了基础。Economic Viability. An adopted vision plan that provides urban design recommendations to overcome Houston’s absence of zoning as well as social, economic, and environmental issues was critical for the district. Reinvestments grew exponentially, setting the stage for Midtown Park.
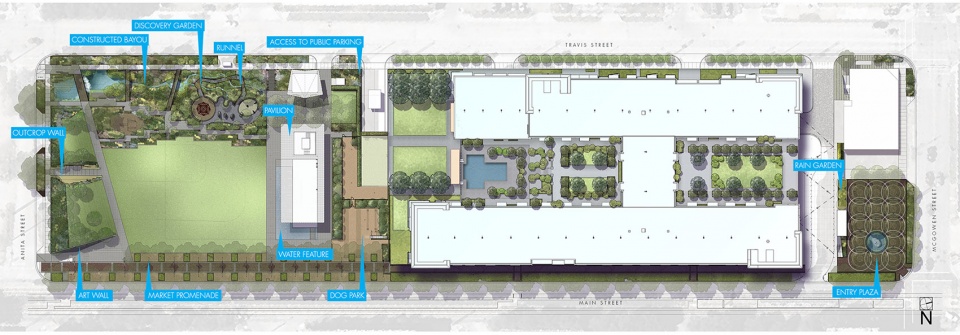
▲场所营造。在中城重建局(MRA)作为一个改革机构在休斯顿成立时,中城“中央公园”的概念就已经启动。场所营造和复原力被认为是该项目能够成功落实的关键因素。Placemaking. The concept of a “central park” for Midtown was set in motion when the Midtown Redevelopment Authority (MRA) established itself as an agency of change in Houston. Placemaking and resilience were identified as critical success factors for this project.

▲功能布局:中城公园由各种灵活的多功能空间构成,可以容纳丰富的活动和计划,如日间集市和节庆活动等,它们为周边社区创造了经济增长,并树立了社区意识。Programming. Midtown Park is comprised of a wide variety of flexible, multi-functional spaces that can accommodate several events and programs such as day markets and night festivals, which create economic growth and a sense of community within the surrounding neighborhood.

▲环境管理:标志性的“河湾”设计是一个人工建造的水道和滞留系统,模仿了休斯顿的天然河口湿地和低地沼泽。这一具有教育功能的元素反映了该地区的自然水文生态系统。Environmental Stewardship. The signature design feature, the “Bayou”, a constructed water channel and detention system, which mimics the natural bayou wetlands and bottomland swamps of Houston. This educational component reflects the natural hydrologic ecosystem of the region.
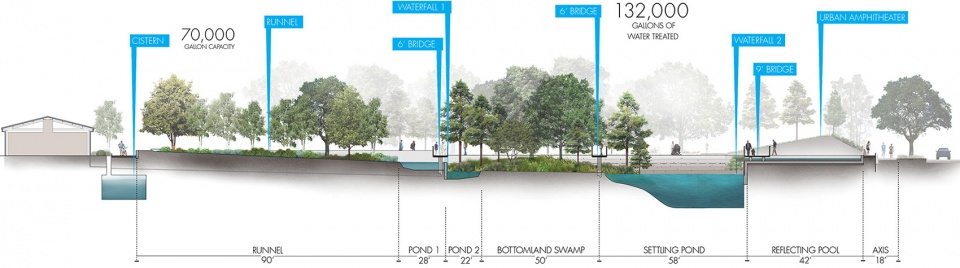
▲可持续性:雨水被收集并储存在一个容量为7万加仑的地下蓄水池中。中水被用于灌溉或再循环。多余的水将直接流入建造好的河湾,在那里停留一段时间后再排入城市的雨水沟渠系统。Sustainability. Rainwater is collected and stored within a 70,000-gallon subsurface cistern. The greywater is used for irrigation or recirculation. Excess water flows directly into the constructed bayou, where it is held before release into the municipal storm sewer system.

▲恢复力:中城公园的河湾在改善水质和野生动物栖息地的同时,还能够防止洪水泛滥,从而增强经济与生态复原力。在极端降雨事件发生期间,河湾可以吸收并滞留雨水,从而防止当地洪泛和财产损失。Resilience. The Midtown Park Bayou establishes ecological resiliency by protecting against flooding while improving water quality and wildlife habitat. During extreme rainfall events, the bayou can absorb and detain stormwater preventing local flooding and property damage.

▲环境敏感性:公园的设计创造了一个能让树木和花园茁壮生长的环境。地下停车场的上方是一个具有生命力的、可持续的公园,它拥有复杂的排水系统、坚固的防水层、水泵和雨水蓄水池。Environmental Sensitivity. The park design creates an environment where trees and gardens thrive in adequate soil volumes. A living, sustainable park above an underground parking garage with an intricate system of draining capabilities, robust waterproofing, pumps, and a rainwater cistern.
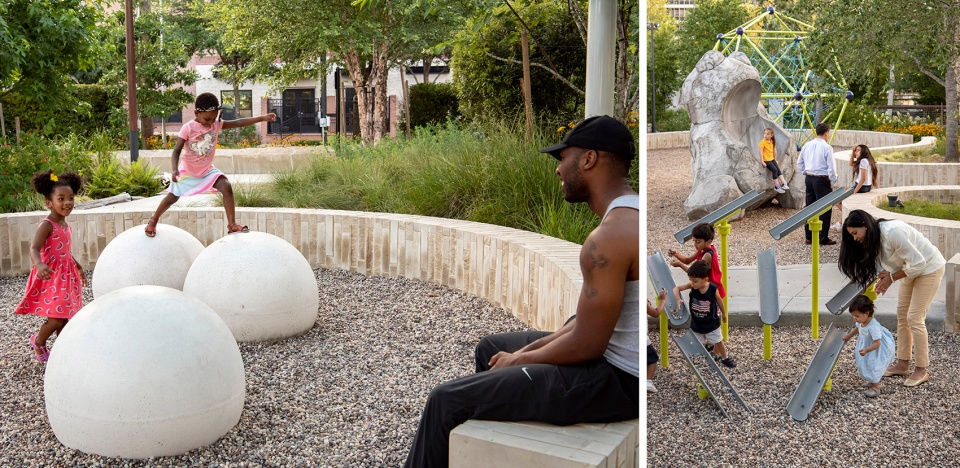
▲多样性、公平性和包容性:中城公园是为所有年龄段和文化背景的人而设计,包含小径、游乐场和互动喷泉。位于舞台旁边的“雨水喷泉”通过“雨滴”和“闪电”的场景编排来模拟休斯顿的暴风雨。Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion. The park is designed for all ages and cultures. There are trails, playgrounds, and an interactive fountain. The “Rain Fountain” located adjacent to the stage is designed to mimic a Houston storm event by choreographing “rain drops” and “lightning”.
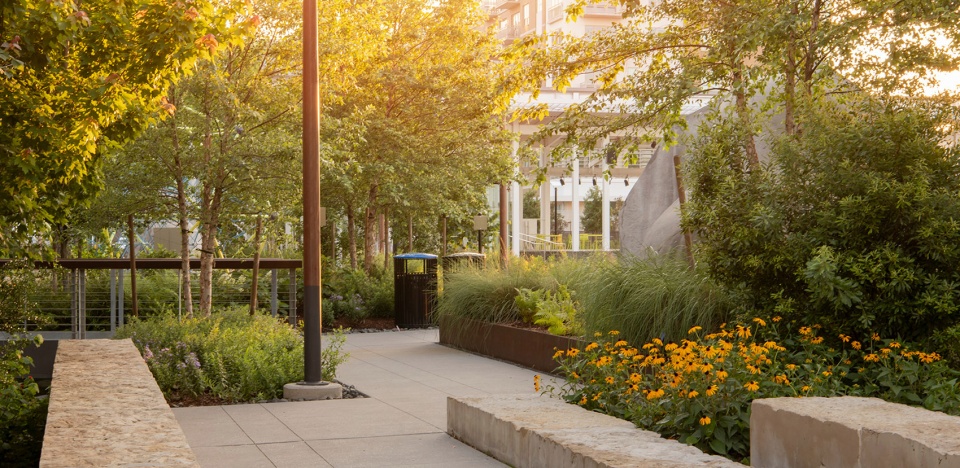

▲城市本地花园:80多种本地落叶乔木、林下灌木、芳香授粉植物和湿地植物,为改造后的城市环境注入了多样且活跃的生态。由本地石凳围成的线性小径为河湾沿岸提供了休憩的机会。Urban Native Gardens. Over 80 species of native deciduous trees, understory shrubs, fragrant pollinators, and wetland plants, infuse diverse and vibrant ecologies into the transformed urban setting. Linear pathways, bound by native stone benches, offer opportunities for respite along the Bayou.
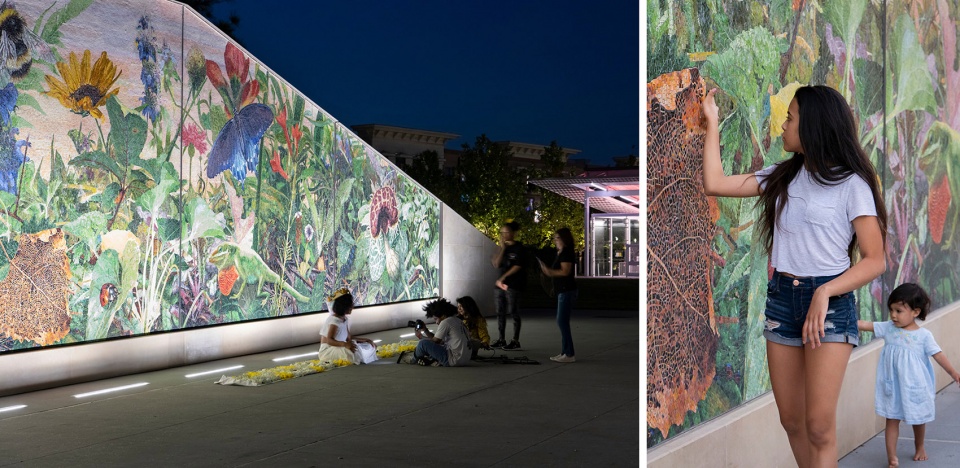

▲艺术与文化。公共艺术是整个公园中的重要元素。中城公园保护协会投入巨资,邀请来自当地且在国际上知名的艺术家设计了4件永久艺术作品,使公园成为该地区标志性的存在。Art and Culture. Public art is a key element seen throughout the park. The Midtown Parks Conservancy made significant investments in securing local, internationally recognized artists to install four permanent art pieces, cementing the park as an icon for the district.
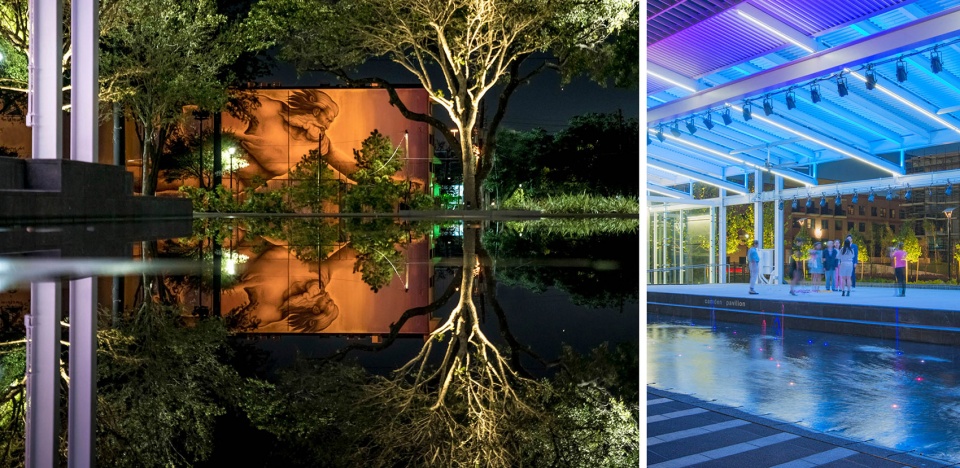

▲对水的赞美:公园的设计同时回应和拥抱了休斯顿的酷暑天气。在舞台旁边,一层薄薄的水面能够在白天为主广场区域降温,到了夜晚则变成一个充满艺术感的反光元素。Celebrating Water. The park design not only responds to, but embraces, the intense heat of Houston. Adjacent to the stage, a thin sheet of water cools the primary plaza area during the daytime, while at night, becomes a reflective, artful element.

▲交通和基础设施:中城公园拥有便捷的公交系统,包括公共汽车、轻轨、自行车共享系统和现场滞留空间,长期保持着公平性和可达性,并迅速成为了该区最受欢迎和游览频率最高的开放空间之一。Transit and Infrastructure. With immediate access to transit: buses, light rail, and bike share systems and onsite detention, Midtown Park has remained equitable and accessible, and it quickly became one of the most popular and frequented open space destinations in the district.
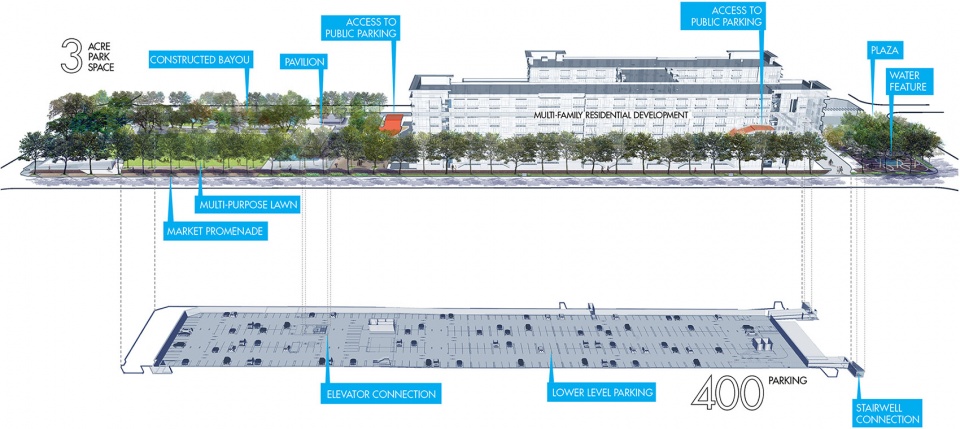
▲使开放空间最大化。设计整合了一个可容纳400个车位的地下车库,为该项目提供了必要的停车空间,使其在可用土地十分有限的地区也具有可行性。占地三英亩的公园最终得以为打造充满活力的社区空间做出贡献。Maximizing Open Space. The design integrates a 400-space subterranean garage, which offers the necessary parking to make the project viable in a district with limited available land, enabling the three-acre park to contribute towards creating a vibrant community space.
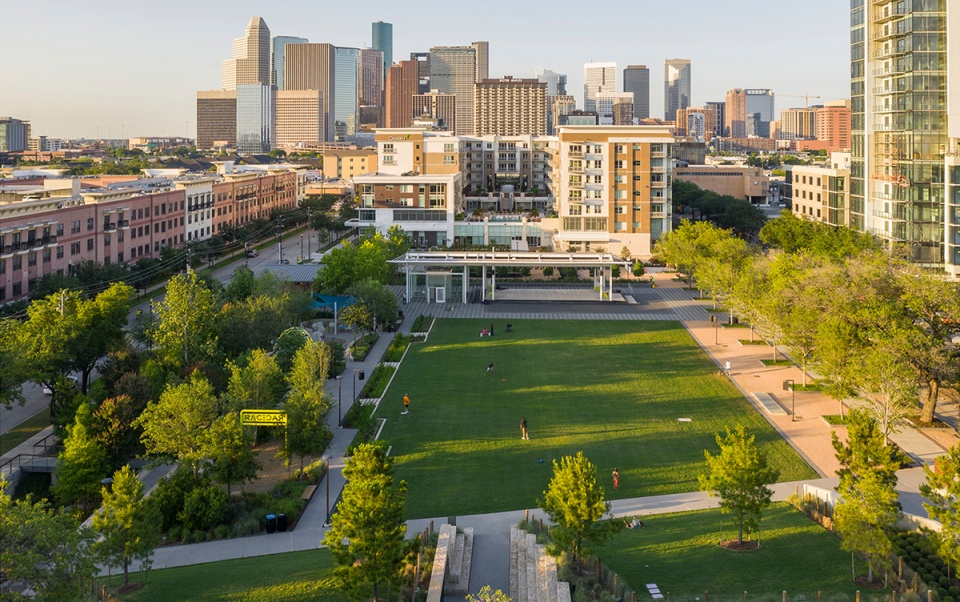

▲促进更广阔的城市景观:作为中城区最重要的公园景点,成功整合高度复杂的雨水管理系统,并承诺以负责任的方式使用资源,对于该项目有着至关重要的意义。公园的可持续发展措施为休斯顿市民提供了一种全新模式。Contributing to the Broader Urban Landscape. As the premier park destination in Midtown, successful integration of highly complex stormwater management systems and a commitment to the responsible use of resources is vital for the larger district. The park’s sustainability measures offer a new model to Houstonians.
Project Narrative
Many know Houston as the commuter, flood-prone city without zoning. Fewer know it as the most diverse city in the United States. The design team was commissioned by the Midtown Redevelopment Authority (MRA) to reimagine and rebrand the district as a vibrant pedestrian-oriented, mixed-use hub. Through strategic planning efforts and a collection of catalyst project investments, Midtown is now considered the most walkable place to live in Houston. Midtown Park, the culminating effort, provides residents and visitors a true urban park.
Over the last fifty years, many attempts were made to revitalize Midtown. However, a lack of distinguishable community character and identity as well as aging infrastructure continuously saw businesses move to the cost-effective suburbs. In the 1990s, grassroots efforts formed the MRA, an organization dedicated to the growth and prosperity of the district. The MRA immediately petitioned the city to define Midtown as an arts and entertainment district supported by a Tax Increment Reinvestment Zone (TIRZ). This set the stage. Midtown, with its superb location, TIRZ support, and new designation, was ready to reach its full potential.
A holistic revitalization effort commenced in 2010 with a Livable Center Study, which sought to recommend strategies that could breathe new life into the Midtown District. The design team prepared a vision plan focused on identifying urban design mechanisms and pilot projects that would help the community address social, environmental, and economic issues as well as showcase the arts. The plan also provided recommendations to overcome Houston’s absence of zoning and aging infrastructure. The design team identified placemaking and resilience as critical success factors for catalytic implementation projects. The capstone of these projects, Midtown Park, is the premier destination for the (now) “most walkable neighborhood” in Houston.
VISION
The concept of a “central park” in Midtown was set in motion when the MRA established itself as an agency of change in Houston. MRA worked to acquire underutilized properties to capitalize on this opportunity. Upon acquisition, the MRA, developer, and design team worked in partnership over several years to develop the property into a hub of activity for the district.
CONTEXT
Midtown Park is the epicenter of Houston’s Midtown District, a growing neighborhood with renewed identity from public realm redevelopment. The 6-acre project site is a “superblock” created from inaccessible, privately owned, and unmaintained open fields, bounded by narrow sidewalks and several large existing oak trees, which were preserved and protected. The centerpiece of the property and larger parks system is Midtown Park, a 3-acre parcel activated with a performance pavilion, trails, marketplace, playgrounds, interactive fountain, an arts garden, dog park, and social game courts. Bayou-inspired water features bring nature to the city providing respite and sustainable water management – all built on top of a public underground parking garage. Midtown Park is a demonstration for the continued development of a greener, more walkable Houston that proves that high-quality public spaces are a crucial ingredient for successful, livable cities.
Challenged with creating the “premier urban park destination in Midtown”, the design team understood the park needed seamless integration into the district. They capitalized on the site’s geographic locale, proximity to transit, surrounding developments, and a need to place parking below grade. The design team successfully collaborated, designed, and implemented a park that serves the needs of the neighborhood and greater community as well as bolstered the integrity of the district’s brand through programming and innovative design features.
Midtown sits between two major employment hubs, Downtown and the Medical Center. The district made public streetscape investments in Midtown to foster growth. This increased walkability as well as demand for accessible park space; therefore, Midtown Park is a critical destination within the urban fabric of Houston, a city with one of the lowest Park Scores in the nation.
FEATURES
The location of the park immediately adjacent to Houston’s transit-oriented Main Street was strategically identified by the design team to ensure Midtown Park remained an equitable resource. With immediate access to transit, light rail, and bike share systems, Midtown Park has quickly become one of the most popular and frequently visited open spaces in the district, and park visitors exemplify Houston’s title as the most culturally diverse city in the United States.
Midtown Park is comprised of a wide variety of flexible, multi-functional spaces that can accommodate several events and programs such as markets and festivals, which create economic growth and a sense of community within the surrounding neighborhood. In support of the Midtown Strategic Plan and the Midtown Open Space Plan, the design of the park engages all age groups. To aid the continual evolution of the park, the design and layout focuses on flexible use, utilizing the large, centrally located, multi-purpose lawn, which is gently sloped to face the “Rain Fountain” adjacent to the stage. When not operational, the Rain Fountain (designed to mimic a Houston storm event by choreographing “rain drops” and “lightning”) can be transformed into additional plaza space for flexible seating during events.
Public art is a key component of the park’s design, and it can be seen throughout the park. The Midtown Parks Conservancy made significant investments in securing local, internationally recognized artists to install 4 permanent art pieces, cementing the park as an icon for the district.
The berms, just behind the event lawn, provide topographic relief in an area with unremarkably flat topography that provide views of Downtown’s skyline. Despite the berms, the park, with superb lighting, maintains a sense of transparency from corners and key pedestrian edges, such as Main Street, allowing the park to reach beyond its borders into the diverse community.
A challenge that proved surmountable was creating an environment where trees and gardens could thrive in adequate soil volumes and uphold a living, sustainable park above an underground parking garage with an intricate system of draining capabilities, robust waterproofing, pumps, and a rainwater cistern. The underground parking garage presented both an opportunity and a challenge, as the integration of much-needed parking helped to make the project viable in an area that is under extreme development pressure with little desire for surface lots.
RESILIENCE
The backbone of the site and key feature of the design was the integration of the “Bayou”, a constructed water channel and detention system, which mimics the natural bayous, swamps, bottomland hardwood forests and wetlands of Houston, all of which are integral pieces of the hydrology of the region. Working together with bioswales and rain gardens, these educational features were designed with an assortment of native plant materials typically found in this environment and has proven to enhance economic and ecological resiliency by protecting against flooding while improving water quality and wildlife habitat. During extreme rainfall events, like Hurricane Harvey, the bayou can absorb and detain stormwater preventing local flooding and property damage.
Rainwater is collected and stored within a 70,000-gallon subsurface cistern. The water is reused on-site for irrigating plant material or as “make-up” water for the recirculating Midtown Bayou. When there is excess water, such as during large rain events, an overflow structure moves water directly to the constructed bayou, where it is held and treated by the plants and soils before release into the municipal storm sewer system. This layered and integrated approach to stormwater management takes pressure off over-burdened infrastructural systems and helps to cleanse water through natural infiltration. As the premier park destination in Midtown, the successful integration of highly complex stormwater management systems and a commitment to the responsible use of resources was vital for the development. The park’s sustainability measures offer a new model to Houstonians – SITES Silver certification.
More: ASLA; Design Workshop, Inc.
扫描二维码分享到微信